Before your broker submits loan capital to allow you to trade the foreign exchange market, you must open a margin account.
Margin is a term that describes deposits in good faith, used by your broker as part of your trade guarantee. Remember, your Forex broker in the business makes money by facilitating trade.
They will not bear losses on your behalf. They will not put themselves in a position where your losses will exceed the amount of money you have in your account.
When you open a margin account with a regulated forex broker, in some ways it is similar to applying for a credit card. Your broker will question the background of your trade including your experience. They want to know how long you have been trading, as well as your investment goals.
Your broker can also ask about the size of a potential account, as well as other accounts that you currently open. All of these questions are used to determine whether they should provide you with a margin account and the type of leverage they offer you.
Your broker will charge interest on the money used in your margin account. So, if you trade EUR / USD that has a notional value of $ 10,000, and borrows $ 9,500, your broker will charge you with a margin interest rate on that balance as long as you have open trade.
After you close the trade, the interest costs stop. The interest rate charged to general margin is the market interest rate.
Before trading using margin, you must find out the rates charged by your broker. If it doesn't match the other market prices, you can consider using another broker. The 5% difference at $ 9,500 for the full year is $ 475.
Remember, you are only billed for margin when your trade is active. For example, if you borrow $ 9,500 for 1 week, at an interest rate of 5%, you will be charged $ 9 = (5% * $ 9,500) / 52.
Please visit our sponsors
Results 1 to 1 of 1
-
10-05-2019, 01:18 PM #1Top Asia Forex Broker Rev

- Join Date
- Jul 2017
- Location
- vanutu
- Posts
- 164
- Feedback Score
- 0
- Thanks
- 0
- Thanked 0 Times in 0 Posts

 What is a Margin Account, and How Do You Use It?
Discover one of the leading Forex trading platform - AssetsFX
What is a Margin Account, and How Do You Use It?
Discover one of the leading Forex trading platform - AssetsFX
-
Sponsored Links
-
Sponsored Links
Thread Information
Users Browsing this Thread
There are currently 1 users browsing this thread. (0 members and 1 guests)
Tags for this Thread
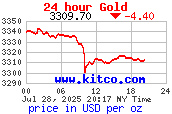
24 Hour Gold
Advertising
- Over 20.000 UNIQUE Daily!
- Get Maximum Exposure For Your Site!
- Get QUALITY Converting Traffic!
- Advertise Here Today!
Out Of Billions Of Website's Online.
Members Are Online From.
- Get Maximum Exposure For Your Site!
- Get QUALITY Converting Traffic!
- Advertise Here Today!
Out Of Billions Of Website's Online.
Members Are Online From.






 LinkBack URL
LinkBack URL About LinkBacks
About LinkBacks


 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote